WebSocket 是一种可实现客户端和服务器之间实时双向数据传输的通信协议。2008年,出现初期概念与需求。2011年实现正式标准化 RFC 6455。2011年及以后快速发展、广泛应用到实时应用场景。WebSocket 的优点是实时、低时延和低带宽。
1. WebSocket 如何工作
WebSocket 通过 HTTP 进行 upgrade 握手,将通信协议升级为 ws://(wss://),此后所有通信均通过 TCP 进行。
GET /api/v1/ws?session_id=123456
Origin: https://abc.test.xx
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Key: uRA2WL4ufOJbg5WRI8LGuw==
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
Host: abc.test.xx
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols
Server: XXX
Date: Thu, 05 Sep 2024 00:19:27 GMT
Connection: upgrade
Upgrade: websocket
Sec-WebSocket-Accept: kpStiDhj1d43uiPN/tKkDGQTgEE=
Sec-WebSocket-Accept 的计算方法:
- 将 Sec-WebSocket-Key 跟 258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11 拼接;
- 通过 SHA1 计算出摘要,并转成 base64 字符串。
2. 网络层适配
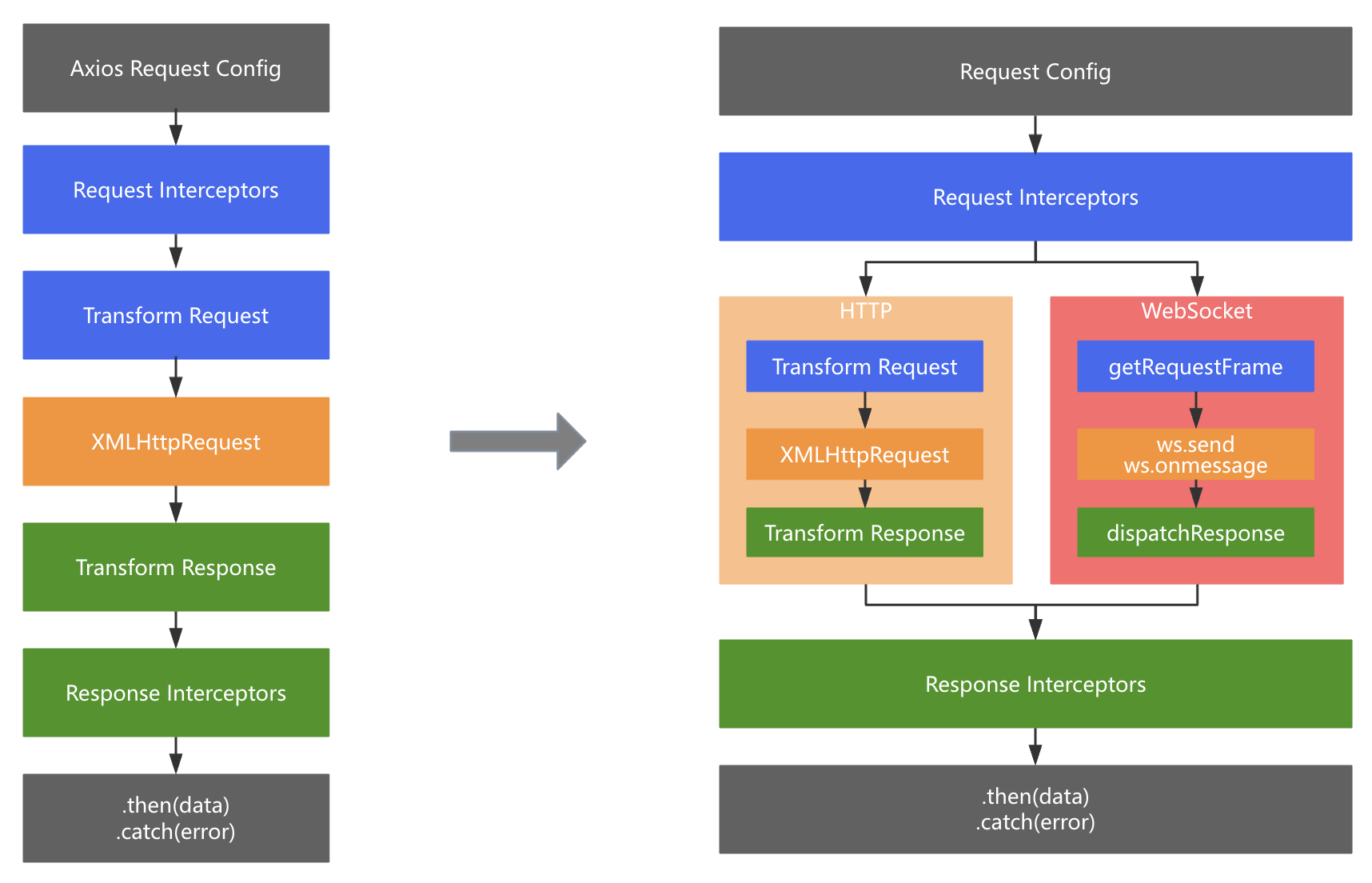
项目里已经使用 Axios 处理 HTTP 请求,接入 WebSocket 最好复用已有的 Interceptor 和 Callback 逻辑,降低开发和维护成本。
2.1 WebSocket 消息协议格式
- seqId:请求消息 ID,对应的响应消息 ID 与之相同
- msgType:消息类型,包括普通消息、ping 和 pong
- content:包含请求 wsProxyHttpRequest 和响应 wsProxyHttpResponse
{
"seqId": 1725240629225,
"msgType": 2,
"content": {
"wsProxyHttpRequest": {
"path": "/api/v2/solution",
"method": "GET",
"query": "intent_id=3226&session_id=123456"
}
}
}
{
"seqId": 1725240629225,
"msgType": 2,
"content": {
"wsProxyHttpResponse": {
"statusCode": 200,
"response": "{\"code\":0,\"msg\":\"success\",\"data\":{}}",
"responseHeaders": {
"Trace-Id": "1a7cee4721192633ecc8e0475fd43602",
"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=utf-8"
}
}
}
}
2.2 链式调用
Axios 实现:
/**
* Dispatch a request "version": "0.19.2"
* @param {Object} config The config specific for this request (merged with this.defaults)
*/
Axios.prototype.request = function request(config) {
// Allow for axios('example/url'[, config]) a la fetch API
if (typeof config === "string") {
config = arguments[1] || {};
config.url = arguments[0];
} else {
config = config || {};
}
config = mergeConfig(this.defaults, config);
// Set config.method
if (config.method) {
config.method = config.method.toLowerCase();
} else if (this.defaults.method) {
config.method = this.defaults.method.toLowerCase();
} else {
config.method = "get";
}
// Hook up interceptors middleware
var chain = [dispatchRequest, undefined];
var promise = Promise.resolve(config);
this.interceptors.request.forEach(function unshiftRequestInterceptors(
interceptor
) {
chain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
this.interceptors.response.forEach(function pushResponseInterceptors(
interceptor
) {
chain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected);
});
while (chain.length) {
promise = promise.then(chain.shift(), chain.shift());
}
return promise;
};
Axios 原型上的 Request 函数实际上是调用 Axios.get、Axios.post 发送 HTTP 请求时都会调用的函数。函数上面部分处理请求的 Config 可以略过,重点看下面的部分。
- 首先初始了一个 chain,也就是
调用链。有 dispatchRequest 和 undefined。dispatchRequest 就是实际发送请求的函数。 - 跟着初始化了一个 resolve 请求的 Config 的 Promise。
- 然后是把请求的拦截器塞到了
调用链的前面,再把响应的拦截器放到了调用链的后面。调用链准备完毕之后,调用 while 循环把调用链用 promise 串起来,最后返回 promise。
借鉴 Axios 调用链 的实现,对 WebSocket 的请求和响应也做类似的处理。
async function send(requestParams, successCallback, errorCallback, finalCallback) {
if (this.isWebSocketOpen) {
const { seqId, request, params } = requestParams;
let modifiedConfig = getRequestConfig(apiConfig, params);
for (let index = 0; index < this.requestInterceptors.length; index++) {
modifiedConfig = await this.requestInterceptors[index](modifiedConfig);
}
const requestFrame = getRequestFrame(seqId, modifiedConfig);
try {
const buffer = getRequestBuffer(requestFrame);
// 回调和超时控制
this.requestInfoMap.set(seqId, {
config: modifiedConfig,
callbacks: [successCallback, errorCallback, finalCallback],
timer: needClearSetTimeout(() => {
errorCallback();
finalCallback();
const requestInfo = this.requestInfoMap.get(seqId);
if (requestInfo) {
requestInfo.isTimedOut = true;
}
}, REQUEST_TIMEOUT),
isTimedOut: false,
});
this.socket.send(
buffer.buffer.slice(buffer.byteOffset, buffer.byteOffset + buffer.length)
);
} catch (e) {}
} else {
this.reconnect();
}
}
export function dispatchResponse(
responseContent: ResponseContent,
config: RequestConfig,
devInfo: Record<string, any>
) {
try {
const res = JSON.parse(responseContent.response);
const status = responseContent.statusCode;
if (status >= 200 && status < 300) {
if (devInfo.wsAckTime && res.time_consuming) {
devInfo.wsNetworkTime = devInfo.wsAckTime - res.time_consuming;
}
return Promise.resolve({
status,
data: res,
config,
devInfo,
});
} else {
return Promise.reject({
status,
config,
response: {
status,
data: res,
},
});
}
} catch (error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
}
}
handleResponse(
responseContent: ResponseContent,
config: RequestConfig,
devInfo: Record<string, any>
) {
const responseInterceptorsChain = [] as any[];
this.responseInterceptors.forEach((interceptor) => {
responseInterceptorsChain.push(
interceptor.fulfilled,
interceptor.rejected
);
});
const len = responseInterceptorsChain.length;
let promise = dispatchResponse(responseContent, config, devInfo);
let i = 0;
while (i < len) {
promise = promise.then(
responseInterceptorsChain[i++],
responseInterceptorsChain[i++]
);
}
return promise;
}
this.socket.onmessage = (event) => {
const rawData = event.data;
let responseObject;
try {
responseObject = getResponseObject(rawData, true);
} catch (error) {
return;
}
// 处理 pong 则 return
const seqId = responseObject.seqId;
if (this.checkResponseTimeout(seqId)) {
return;
}
const requestInfo = this.requestInfoMap.get(seqId);
store.sessionStore.seqIdToAckMap.delete(seqId);
if (requestInfo?.callbacks?.length) {
const [successCallback, errorCallback, finalCallback] =
requestInfo.callbacks;
this.handleResponse(
responseObject.content?.wsProxyHttpResponse || {},
requestInfo?.config
)
.then(successCallback, errorCallback)
.finally(finalCallback);
this.requestInfoMap.delete(seqId);
}
};
2.3 重连设计
WebSocket 的连接由 connect 开始,由于各种原因 WebSocket 可能断开连接,需要重连。这里添加了重连次数的限制,超过限制则不再重连。
对于交互流程是一来一回的简单业务,直接使用了原生的 WebSocket API,结合采用了 Protocol Buffers (简称PB) 这种二进制的序列化协议。
connect(openCallback?: Function) {
if (this.numberOfConnectLeft <= 0) {
return;
}
this.socket = new WebSocket(this.url);
// An ArrayBuffer would have to be fully read before it
// could be used, and all of the data would have to be
// in memory at the same time. In contrast, a Blob can
// be read as a stream, avoiding having to have all
// the data in memory before you can do anything with
// it (or at all).
this.socket.binaryType = 'arraybuffer';
this.closeTimer = needClearSetTimeout(() => {
this.close();
this.isEnabled = false;
}, REQUEST_TIMEOUT) as unknown as number;
this.socket.onopen = () => {
if (!this.isEnabled) {
return;
}
if (this.closeTimer) {
clearTimeout(this.closeTimer);
}
if (this.reconnectTimer) {
clearTimeout(this.reconnectTimer);
}
openCallback?.();
this.ping();
};
this.socket.onmessage = (event) => {
// handle response
};
this.socket.onclose = (e) => {
this.reconnect();
};
this.socket.onerror = (e) => {
this.reconnect();
};
this.numberOfConnectLeft--;
}
除了限制链接次数,对 WebSocket 的连接耗时也做了限制,超时连接不上则直接禁用。连接成功后就开始发 ping 消息。ping 后超时未收到 pong 的话,就会重连。WebSocket 是有自己的 ping pong 消息协议的,为什么我们自己还要实现 ping pong 呢?原因是因为客户端和服务端之间隔了个网关,需要用业务的 ping pong 保证请求链路是通的。
说完 ping pong,看下重连,在 WebSocket 状态未打开、有报错和被动关闭的时候,都需要重连。
async reconnect() {
const { isConnected } = await fetchNetworkInfo();
if (
!this.isEnabled ||
!isConnected ||
this.isReconnectScheduled ||
this.isWebSocketConnecting
) {
return;
}
this.isReconnectScheduled = true;
this.reconnectTimer = SetTimeout(() => {
this.connect(tryToPullLostWSMessage);
this.isReconnectScheduled = false;
this.reconnectTimeout += RECONNECT_TIMEOUT_INCREASE_UNIT;
}, this.reconnectTimeout);
}
客户端通常会一起收到 error 和 close 事件,所以重连方法有必要设置一个锁,如果已经存在一个重连的定时器,那就不要再创建了。
另外在因连接超时被禁用、断网和 WebSocket 正在连接中的时候,也不需要重连了。
